One of the best qualities of milk is that one can turn it into numerous other products through processing. It’s a great opportunity for small dairy farms to offer their customers a wider choice of options after initially only producing milk. Fortunately, you don’t need a whole milk processing factory to offer different dairy goods. In this article, you will find out everything you need to know about small-scale dairy processing.

Small-Scale Milk Processing
You can get numerous dairy products through milk processing:
- Cream
- Butter
- Pasteurized milk
- Yogurt
- Cheese
- Ice cream
- Fluid milk
- Buttermilk
- And other products
Almost every small farm processes milk to make it pasteurized because it’s forbidden to sell raw milk in most countries. To achieve that, milk is heated in pasteurizers — special devices for pasteurization — and then cooled down. This process destroys disease-causing microorganisms to make milk safer. Also, pasteurization increases the shelf life of dairy products. That’s why most governments demand that both large manufacturers and small farms process their milk to make it pasteurized.
However, pasteurization is a basic process that comes before any other processing you’ll be putting the milk through. And while it’s not mandatory for all countries to pasteurize milk, most farmers still tend to do it because of the increased shelf life.
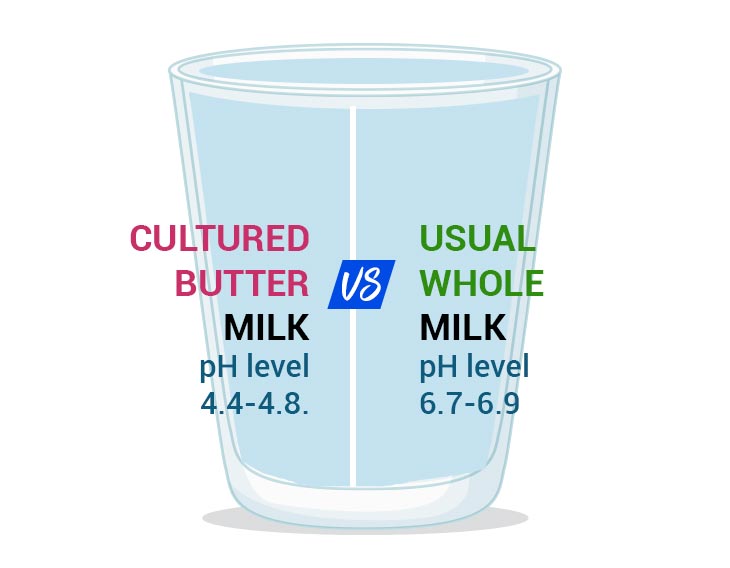
The real processing that will turn milk into another dairy product will include some kind of churning or fermentation. For example, butter is made through the churning process that makes fat clump into butter, discharging the liquid — that’s what we call buttermilk. And to create yogurt, you’ll need to add active cultures to milk and keep it in a warm place until it gets fermented.
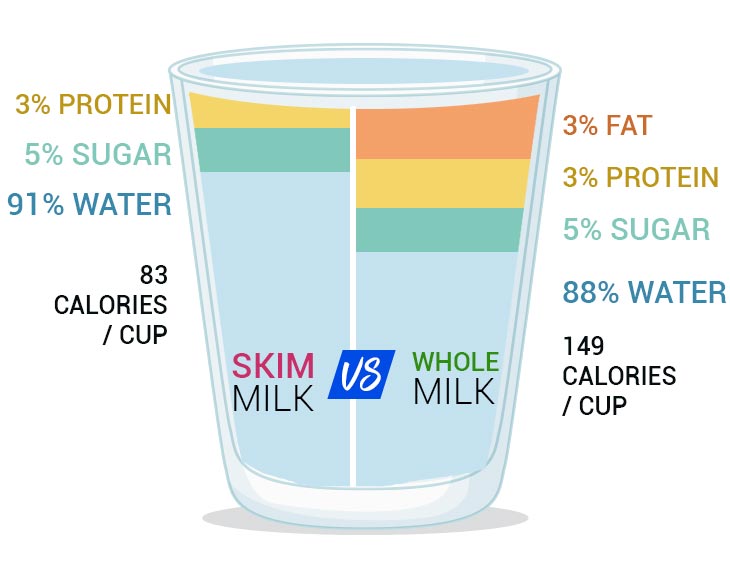
Also, one can make low-fat and skim milk through processing to cover the needs of customers who don’t like or can’t consume whole milk. While whole milk has over 3.25% of milk fat, low-fat milk has from 0.5% to 2.0% of fat. Skim milk contains less than 0.5% of milk fat.
Milk Processing Equipment for Small-Scale Dairy Farm
Now let’s take a look at all the equipment you can get to create your milk processing farm.

Milk tanks
Pre-stack tanks, milk tanks, interim tanks, and mixing tanks are used to store liquid dairy products to keep them fresh for as long as possible. Therefore, they are crucial pieces of equipment for milk processing if you want to produce high-quality, fresh, and safe products.

Pasteurizers
As we’ve already mentioned, pasteurization often lies at the core of milk processing. Pasteurizers are machines that will simplify this step for you. A milk pasteurization unit will heat the milk and keep it at a set temperature for a set duration, stirring it continuously and then cooling it down to make it ready for storing or further processing.
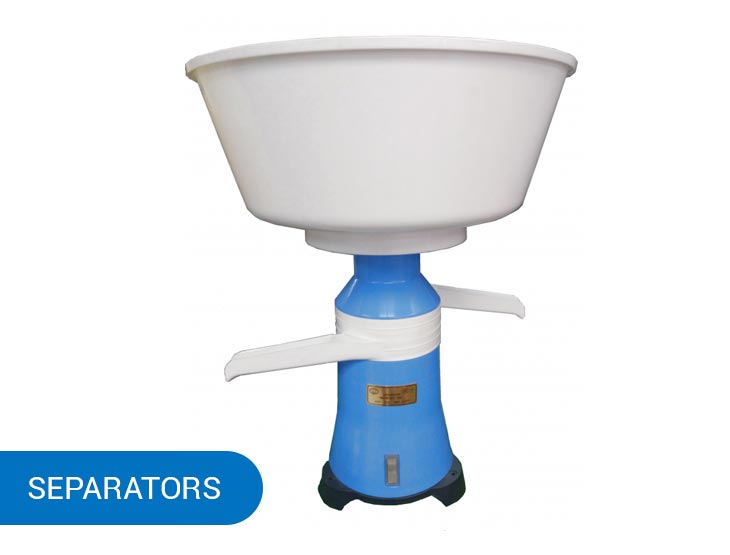

Cream Separators
These machines are used for making low-fat and skim milk and cream. As a cream separator divides fat from milk, you get two products simultaneously — cream and milk that has a lower fat percentage. Depending on the working time of the cream separator, you can get milk and cream of different fat percentages.
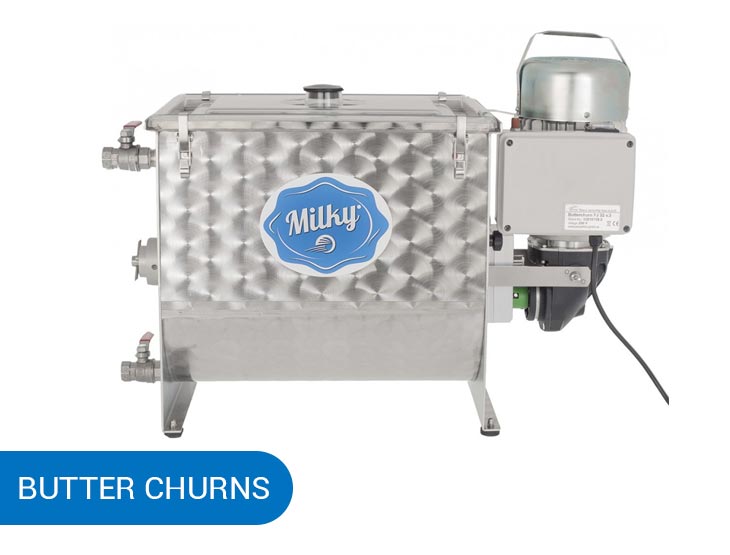

Butter churns
This milk processing device will churn milk into butter, leaving you with two products — butter and buttermilk. The second one is just as popular as butter, and you can sell it right away or ferment it to add more nutrients.
Cheese presses
It’s a very simple device that will apply pressure to cheese curds to squeeze out all the liquid and form cheese. You should choose a cheese press depending on the amount of the dairy product you’re planning to produce.
Homogenizers
This device improves the texture and taste of milk by making it more homogenized. The machine does it by squeezing milk through small holes under pressure, making the cells break apart and homogenize. Usually, this tool is used when you have milk from different cows and you want to make it more consistent.
How’s yogurt made?
It’s made through fermentation — you need to add special yogurt cultures to milk and keep it at a certain temperature for a while to activate the cultures. You can do that using a milk pasteurizer that supports low temperatures. A pasteurizer will be suitable for other fermented dairy products (e.g. fermented buttermilk, sour cream or kefir).
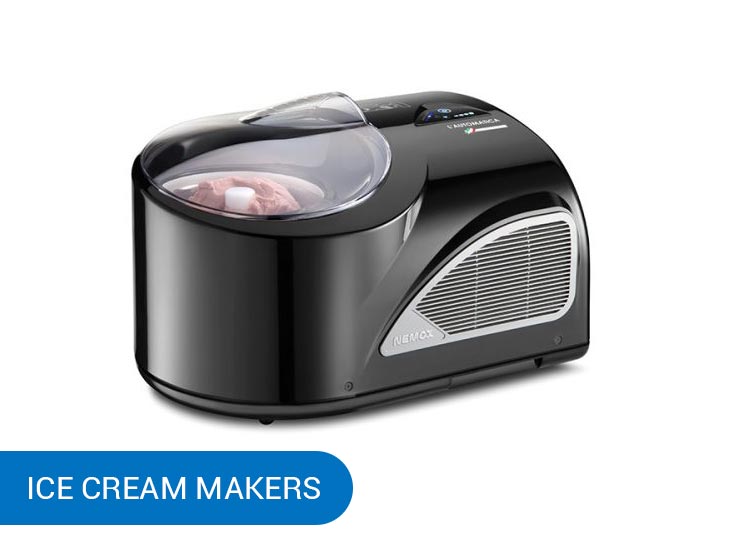

Ice cream makers
This machine is used in milk processing to make ice cream. It will churn the ice cream base slowly while cooling it down. The process creates ice cream with a smooth and creamy texture. No lumps or shards of frozen liquid.
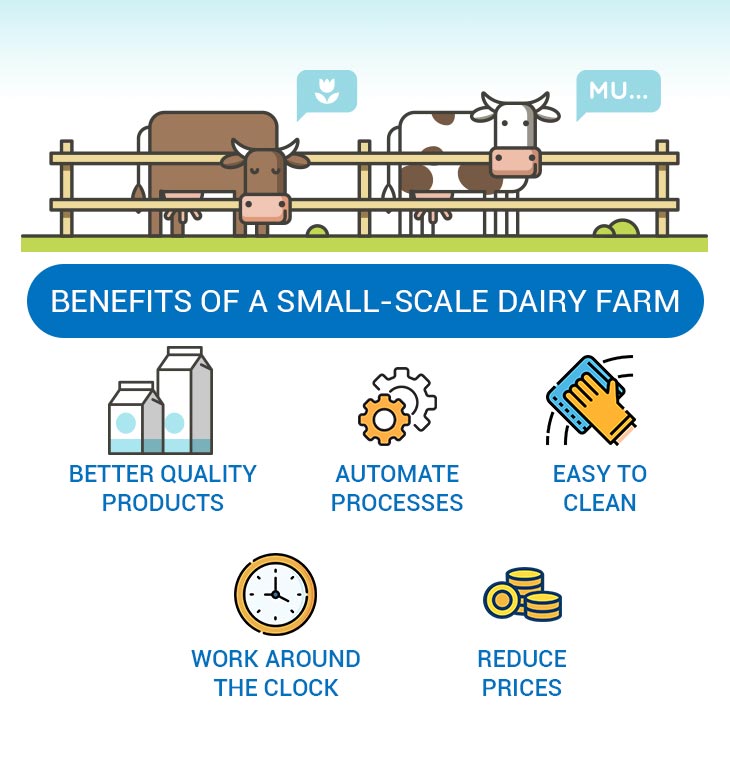
Benefits of a small-scale dairy farm
Sure, there is less hassle in selling simply milk. But dairy processing machines will give you much more freedom and let you make more revenue from your farm. Here are all the benefits you’re getting if you have a small-scale dairy farm:
- You have products of better quality — Homogenizers, pasteurizers and milk tanks will help you improve the overall quality of your dairy.
- Machines automate processes — Therefore, making dairy goods other than milk will not be a hassle. The equipment allows you to create products quicker and more easily while keeping the quality on point.
- It’s easy to clean the machines — Advanced models are made to be easy to clean, so you don’t have to worry about spending hours cleaning the equipment.
- Machines can work around the clock — Of course, there are models that need rest, but you can get equipment that can work 24/7 if you need continuous production.
- You can reduce prices — Since creating dairy products will be less effort-consuming, you’ll have a chance to cut dairy milk processing plant costs and reduce prices to attract more customers.

Even a small farm can offer a variety of products today as equipment becomes more affordable and suited to small-scale production. If you have any more questions about milk processing equipment, just drop us a line and our Milky Day specialists will help you out.