The debate between those who love whole milk and those who prefer the skimmed option is never-ending. Both sides bring good arguments to the table. And you know what? Both sides are right because you have to choose what you like and what works for you.
Going through the internet, you will find numerous articles that discuss how bad skimmed milk is for you. But is it really? It’s not as fatty as whole milk, and that’s about it. So we’re going to balance out all the critical articles about low-fat dairy by sharing the benefits of it with you. And it’s fair to say that skimmed milk has quite a few advantages.

What is skimmed milk?
Before we talk about health benefits, let’s figure out what this product is. The most popular question would be “Is skimmed milk fat-free?” Well, it is almost fat-free, as it contains less than 0.5% fat. It’s virtually impossible to completely get rid of fat in dairy, so some bits of it still remain in skimmed milk.
Let’s compare the fat content:
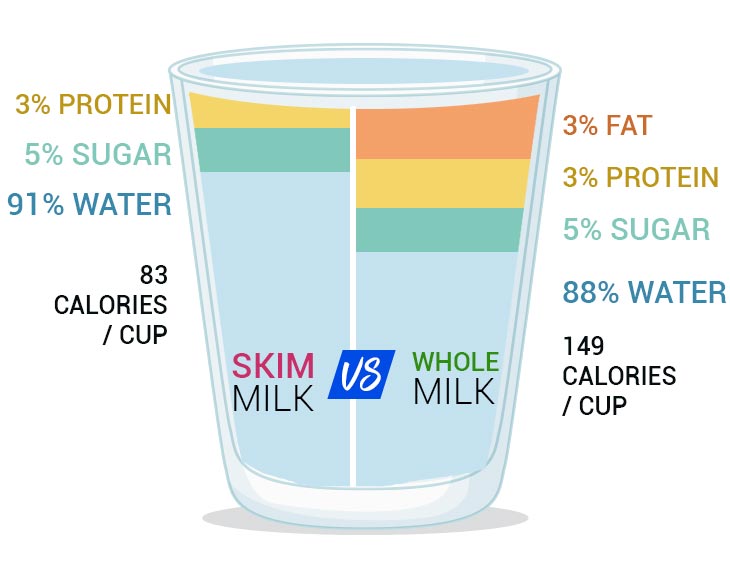
- Whole milk contains 3.5% fat.
- Low-fat milk contains 1-2% fat.
- Skimmed milk contains 0-0.5% fat (it’s mostly around 0.1%).
Depending on where you live, such dairy will be called skimmed, skim, low-fat, fat-free or nonfat milk.
How is skimmed milk made?
Quite obviously by removing fat from whole milk. But how does one get rid of fat? The traditional method is to let milk sit in the fridge and wait until the cream rises to the top and creates a solid layer. Then, as you gather the cream, you will be left with milk with a lower percentage of fat. You will probably need to repeat this process a couple of times to achieve truly skimmed milk, but in essence, that’s how you make low-fat milk.
Of course, modern factories utilize special machinery for this purpose. The device they use is called a separator, and it does just what its name suggests: It separates fat from milk. This machine resembles a large centrifuge that spins at a high speed, forcing cream to gather in the middle and pushing the heavier skimmed milk to the sides. Then, the liquid passes through the holes in the bowl of the separator and gathers in one compartment.
As you can see, the process is quite simple and there are no chemicals involved. That’s why the answer to the question “Is skimmed milk bad for you?” is “No.” It doesn’t become harmful merely because you remove fat from it, even when you use a separator machine for it.
However, some countries require manufacturers to add vitamins to skimmed milk—usually vitamins A and D. Such regulations exist because vitamins dissolve in fat, and as the latter is removed, dairy products lose a fair amount of valuable microelements. Also, manufacturers often add some dried milk to thicken watery skimmed milk. But that’s not something that could harm you.
Skimmed milk vs. whole milk
The debate between fans and haters of skimmed milk is not limited to the health subject. Milk is often used as one of the ingredients in recipes. From this perspective, its taste and consistency matter a lot.
We will be candid here: Whole milk is better than skimmed in most cases if you’re using it for cooking. Low-fat milk will make you a decent latte and it is also quite OK if you pour it into your morning cereal. But to be fair, it sucks when it comes to baking or cooking dishes that require you to heat milk with other ingredients. The lack of fat will make the dairy’s protein stick together and create a clumpy consistency for the dish. This is not the most pleasant consistency to consume. And the lack of fat will make baked goods less shiny and rich-tasting.
Oh, and talking about the taste: Skimmed milk is usually rather watery and tasteless. So if you love that, well, milky taste of whole dairy, the low-fat option won’t be your favorite. However, some people don’t like how whole milk tastes and prefer the taste of skimmed milk. Therefore, it all comes down to personal preference.

5 health benefits of skimmed milk
We will remind you once more that low-fat milk usually doesn’t contain any harmful chemicals and the process of removing the fat involves nothing more than gravity. Therefore, this product is at worst not as beneficial as whole milk since some amount of vitamins are removed with the fat. But it is not harmful. Is skimmed milk good for you, though? Let’s see.
1. For some people, fat is bad
We used to think that fat was bad for everyone until new studies arrived showing that it might not be as bad as we all supposed. Fat is crucial for our body, as it allows us to dissolve and absorb vitamins properly. Also, we receive quite a lot of energy from fat. In fact, some people are able to transform this macronutrient into pure energy much better than carbs, which were seen as a major source of power for the human body. So now we learn to stop being afraid of fat.
However, everything is only good for us in moderation and we are supposed to intake from 44 to 77 grams of fat every day. 200 ml of whole milk contains 7.4 grams of this macronutrient, so that’s quite a lot of fat. If you consumed a lot of fatty products during the day and now you want to treat yourself with a glass of milk, the skimmed option would be a better choice.

Also, people with cardiovascular diseases should consume less fat, as it increases the level of cholesterol—the main cause of heart issues. So for them, skimmed milk would be the only option if they want to consume dairy, as whole milk might actually be quite dangerous for them.
2. Skimmed milk contains more protein
200 ml of whole milk contains 7 grams of this macronutrient, while the same amount of the skimmed option contains 7.3 grams of protein. Sure, 0.3 grams doesn’t look like that much of a difference to us. However, our bodies feel the difference. Studies suggest that the higher level of protein in skimmed milk helps to build muscles much faster than the whole version. Also, low-fat milk contains 18 amino acids, including nine essential ones. These acids are basically building blocks that help us create and maintain lean muscles.
3. There is more calcium
There is 240 mg of calcium in 200 ml of whole milk, compared to 260 mg in skimmed. Calcium is essential for healthy blood flow, bones and teeth. Also, it helps muscles to function properly. To equal a glass of skimmed milk in terms of calcium, you would need to eat 11 servings of spinach, four servings of broccoli or 63 Brussels sprouts. If you ask us, we would prefer to have a glass of low-fat milk.
4. Fewer calories
200 ml of skimmed milk contains only 71 kcal, while the same amount of whole milk contains 130 kcal. That’s twice as many! If you’re trying to get your calorie intake under control, you should favor low-fat milk over whole. However, considering all the benefits we have already listed, we don’t think it will be a difficult decision for you.
5. More phosphorus, potassium and vitamins
200 ml of skimmed milk contains 200 mg of phosphorus and 337 mg of potassium, which is more compared to 198 mg of phosphorus and 323 mg of potassium in the same amount of whole milk. Potassium helps our muscles move properly and keeps our nervous system healthy. And phosphorus helps to build stronger bones and teeth while playing a part in transforming food into energy. Also, skimmed milk often contains more vitamins such as A and D, as manufacturers add them to the product. Therefore, low-fat milk might be even more beneficial in terms of minerals and vitamins than whole milk.

Bottom line
As you can see, there is nothing bad about skimmed milk. It won’t harm your health. In fact, for some people, it will be even more beneficial than whole milk. So it’s up to you to choose which option you prefer. Now that you know all the details about skimmed milk, its advantages and taste features, you can make your own educated decision.
No comments:
Post a Comment